Do video coding impairments disturb the visual attention deployment?
O. Le Meur, A. Ninassi, P. Le Callet and D. Barba
[pdf]
Main Idea
|
|
|---|
|
|
The visual attention deployment in a visual scene is contingent upon a number of factors. The relationship between the observer's attention and the visual quality of the scene is investigated in this paper: can a video artifact disturb the observer's attention? To answer this question, two experiments have been conducted. First, eye-movements of human observers were recorded, while they watched ten video clips of natural scenes under a free-viewing task. These clips were more or less impaired by a video encoding scheme (H.264/AVC). The second experiment relies on the subjective rating of the quality of the video clips. A quality score was then assigned to each clip, indicating the extent to which the impairments were visible. The standardized method DSIS (Double Stimulus Impairment Scale) was used, meaning that each observer viewed the original clip followed by its impaired version. Both experimental results have conjointly been analyzed. Our results suggest that video artifacts have no influence on the deployment of visual attention, even though these artifacts have been judged by observers as at least annoying.
Original figure of the paper
Click on the pictures to look at the original picture.- Figure 1: Key frames for each video sequence used in the test.
- Figure 2: Examples of distortion maps for the sequence called Dancer. From the left to the right: original picture, impaired picture, SSIM distortion map and VQA distortion map (Brighter areas correspond to higher distortions).
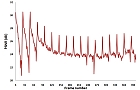
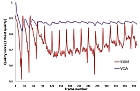
- Figure 3: Temporal evolution of the predicted quality for the sequence Ducks. Three objective quality metrics are used: PSNR (left), VQA and SSIM (right).
- Figure 4: Two stripes extracted from the original (left) and impaired (right) video Dancer (extracted from the impaired picture of the second row of figure 2).
- Figure 6: Saliency map examples: (left) original pictures (Dance first row and Foot second row); (middle) saliency maps; (left) threshold map (threshold=10 for Dance, and threshold=14 for Foot).
- Figure 7: First pictures extracted from clips on which fixation points (blue dots) are superimposed. For each clip, two pictures are given. On the left, fixation points are those obtained on the original video sequence. The right picture for each pair, fixation points are those obtained on the impaired video sequence. (Top) Trees, (Middle) CrowdRun, (Bottom) Ducks.
- Figure 8: Same as figure 7. (Top) Mobcal, (Middle) Parkrun, (Bottom) ParkJoy.






































Supplementary materials
Not yet available.Software
Not yet available.BibTex
@Article{LeMeur_2010,
author = {O. {Le Meur} and A. Ninassi and P. {Le Callet} and D. Barba},
title = {Do video coding impairments disturb the visual attention deployment?},
journal = {Elsevier, Signal Processing: Image Communication},
year = {2010},
volume = {25},
pages = {597-609},
number = {8}
}